What is the Definition of Investment?
An investment is an asset that is intended to produce income or capital gains.
Investing is the act of using currently-held money to buy assets in the hopes of appreciation. Investing is a way to build wealth in the future.
What are Examples of Investments?
There are many investment options, from stocks to jewelry. Essentially, investments can be anything that an investor believes will increase in value over time or produce income (usually in the form of interest or rent).
Stocks
Stocks are an equity ownership. When you buy a stock, you own part of a company. This means that you can profit from a company’s earnings and assets, making stocks an investment.
Bonds
A bond is an agreement between an investor and the company, government, or government agency that issues the bond. When investors buy a bond, they are loaning money to the issuer in exchange for interest and the return of principal at maturity. The bond return makes this an investment option.
Real Estate
Real estate refers to land, as well as any physical property or improvements affixed to the land (including houses). Owning real estate can be considered an investment because it’s possible to build equity over time as well as earn a return on investment from any rent received.
Mutual Funds
A mutual fund can be thought of as a “basket” of investments. Mutual funds provide investors with access to a pool of investment options (e.g. bonds, stocks, equities). This creates a diversified portfolio of investments at a low cost. What’s contained in mutual funds depends on the stated objective of the fund, which varies in risk.
How to Get Started Investing
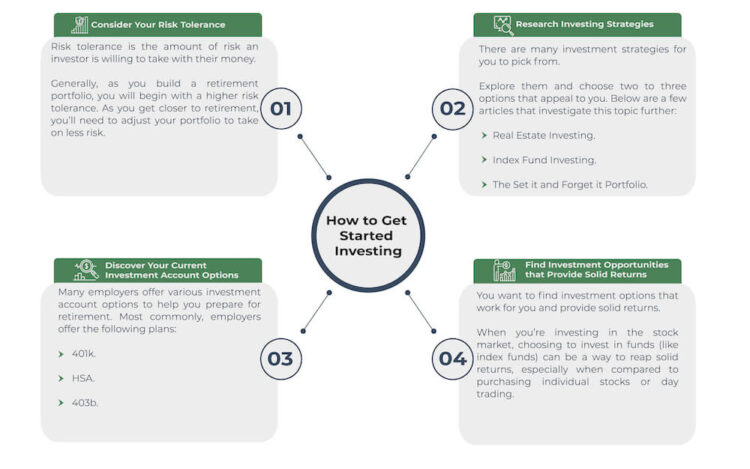
You don’t need to be rich or work on Wall Street to start investing. In fact, the sooner you start investing, the better: You want to maximize your time in the market to reap the returns. Below are the 4 basic steps that will help get you started.
1. Consider Your Risk Tolerance
Risk tolerance is the amount of risk an investor is willing to take with their money. Generally, as you build a retirement portfolio, you will begin with a higher risk tolerance. As you get closer to retirement, you’ll need to adjust your portfolio to take on less risk.
To determine your risk tolerance, consider the following factors:
- Your comfort level with losing money in riskier investments (but having the potential to receive higher returns).
- Your age
- The time left in the market prior to your retirement or withdrawals
2. Research Investing Strategies
There are many investment strategies for you to pick from. Explore them and choose two to three options that appeal to you. Below are a few articles that investigate this topic further:
3. Discover Your Current Investment Account Options
Many employers offer various investment account options to help you prepare for retirement. Most commonly, employers offer the following plans:
If you haven’t already, be sure to ask your HR department about your options. If your employer doesn’t offer any retirement saving options, then you can open an Individual Retirement Account (IRA).
It’s important to note: A retirement account (like a 401k or IRA) is not an investment: The funds, stocks, or bonds held in those accounts are your investments.
4. Find Investment Opportunities that Provide Solid Returns
You want to find investment options that work for you and provide solid returns. When you’re investing in the stock market, choosing to invest in funds (like index funds) can be a simple way to reap solid returns, especially when compared to purchasing individual stocks or day trading.
That’s because index funds track a market “index” (like the S&P 500) which has provided around an 8% average annual return over the past 20 years. Buying individual stocks or day trading is far more challenging to build a diversified portfolio and project potential returns.
What Is Investment Banking?
Investment banking specializes in selling securities and underwriting for new equity shares to help companies raise capital. Investment banking is different from commercial banking (which specializes in deposits and commercial loans).
How Does Investment Banking Work?
Investment banking acts as the middle man between the investor and the company. The investment bank assists with pricing and works to maximize returns.
What is Investment Management?
Investment management is when financial advisors/financial services companies provide investment management by coordinating and overseeing a client's financial portfolio. This could include investments, budgets, accounts, insurance, and taxes.
How Does Investment Management Work?
An investment management company works to substantially grow its client's portfolio.




