What is a Mature Industry?
A mature industry has passed the rapid growth stage and has an established pattern of market share, earnings, and profits.
How Does a Mature Industry Work?
All industries pass through various stages of growth, stability and decline. These phases can be measured in terms of growth, earnings, and profitability. The diagram below illustrates the early stage of a company, emerging with an idea and starting operations, growing its market share and expanding its capacity. After becoming established, a company is mature, gradually slowing its growth, but continuing to improve its profitability. Finally, an industry will begin to decline, losing market, sales, and profits.
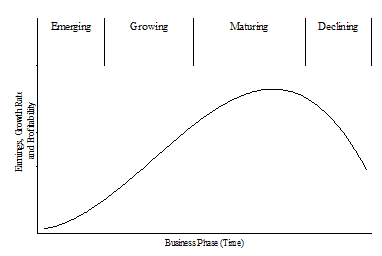
Why Does a Mature Industry Matter?
Each of these industry phases creates new opportunities for investors. Indeed, each phase requires a different type of investor with different expectations of risk and returns. For example, early stage companies provide the largest return potential. However, the risks are usually high and they attract specialized investments through angels or venture capitalists.
The growth phase usually attracts equity investors through established funds. Mature industries typically attract equity (stock) and debt (bond) investors, realizing slower and surer returns. Finally, declining industries can attract a specialized type of investor that focuses on mergers, acquisitions, and other highly leveraged buyouts that can take advantage of the liquidation of business assets.
It is important for an investor to not only know how a company is doing financially, but also what phase of growth, development and decline the company and the industry as a whole are facing.



